Understanding Hormones
Role of Hormones in Human Body
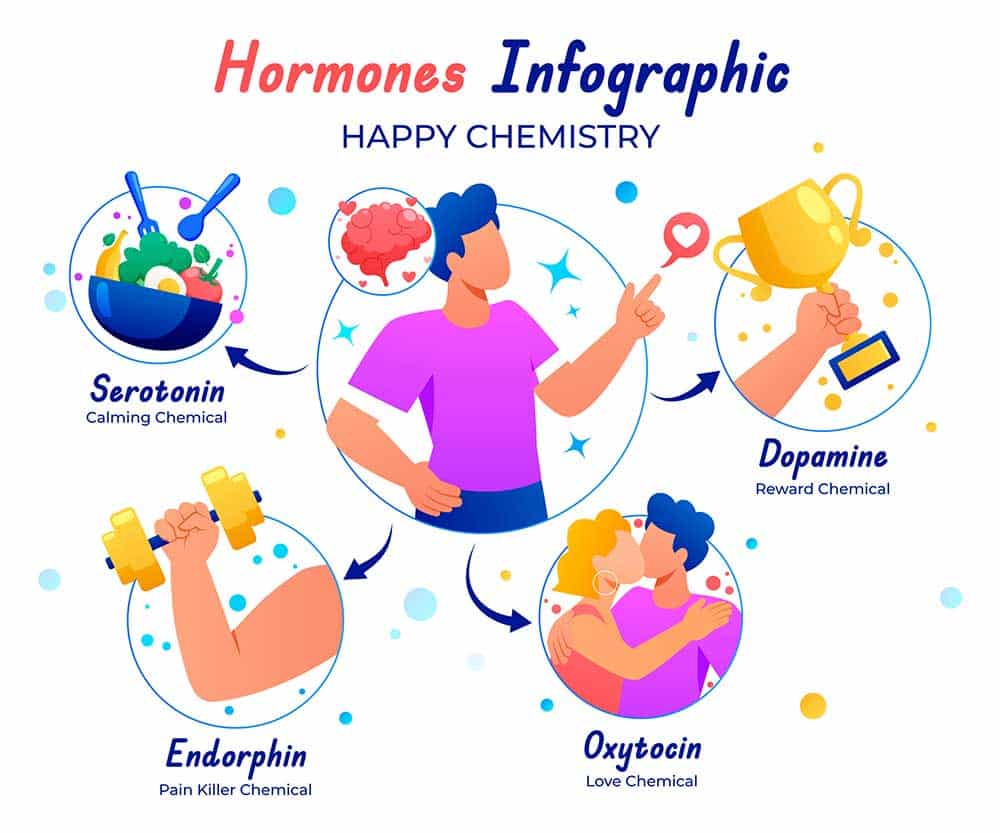
Hormones are essential chemicals responsible for coordinating various functions within the body. These chemicals transmit messages through the blood to organs, skin, muscles, and other tissues, directing the body on what actions to take and when (Cleveland Clinic). Hormones profoundly impact almost every aspect of health by:
- Regulating Metabolism: Hormones like insulin and thyroxine play major roles in managing metabolism and energy production.
- Controlling Growth and Development: Hormones such as growth hormone and estrogen influence physical growth and development.
- Maintaining Homeostasis: Hormones help maintain a stable internal environment, balancing aspects like fluid balance and body temperature.
- Governing Reproductive Processes: Hormones regulate sexual function and reproductive processes.
These functions illustrate the crucial role of the endocrine system and homeostasis in maintaining overall health.
| Function | Key Hormones Involved |
|---|---|
| Metabolism | Insulin, Thyroxine |
| Growth & Development | Growth Hormone, Estrogen |
| Homeostasis | Antidiuretic Hormone, Aldosterone |
| Reproduction | Testosterone, Progesterone |
Importance of Hormone Balance
The human body endocrine system operates by carefully monitoring and adjusting hormone levels. Even minor fluctuations can result in significant responses and health changes. The balance of hormones is vital for several reasons:
- Physical Health: Imbalances can lead to conditions like hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, significantly impacting overall well-being.
- Mental Health: Hormonal imbalances can cause mood swings, anxiety, and depression, affecting mental health.
- Reproductive Health: Hormone levels influence fertility and menstrual cycles, playing a crucial role in reproductive health.
- Metabolic Health: Proper hormone levels are essential for managing weight, energy levels, and appetite, contributing to metabolic health (Cleveland Clinic).
To learn more about how hormones affect metabolic functions, you can explore our article on the role of hormones in metabolism.
An understanding of hormone balance and its significance is crucial when examining common endocrine conditions and how they impact daily life. If you’re interested in the physiological aspects and the anatomy of the endocrine system, check out our article on endocrine system anatomy and physiology. Lastly, for a deeper dive into the different endocrine disorders and common treatments, visit endocrine disorders and treatments.
Key Endocrine Disorders
Understanding the various disorders that can affect the human body endocrine system is crucial for managing health effectively. This section delves into three significant endocrine disorders: Acromegaly, Addison’s Disease, and Diabetes.
Acromegaly and its Effects
Acromegaly is a condition that causes parts of the body to grow unusually large, often affecting individuals in middle age. This disorder is usually due to the overproduction of growth hormone by the pituitary gland. Physical changes are gradual, and early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Enlarged Hands and Feet | Noticeable increase in hand and foot size |
| Facial Changes | Prominent jaw, enlarged nose, and thickened lips |
| Joint Pain | Pain and swelling in joints due to excess growth |
Treating Acromegaly often involves surgery to remove the tumor causing excess hormone production, medication to control hormone levels, or radiation therapy. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Insights into Addison’s Disease
Addison’s Disease occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of cortisol and aldosterone. This insufficiency can lead to severe health issues, given the vital roles these hormones play in maintaining various body functions.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Extreme tiredness and lack of energy |
| Weight Loss | Unintended and noticeable weight loss |
| Low Blood Pressure | Particularly noticeable when standing up |
Diagnosis often involves blood tests to measure cortisol levels and imaging tests to assess adrenal gland structure. Treatment typically includes hormone replacement therapy to compensate for the low production of essential hormones.
Exploring Diabetes Types
Diabetes is a widespread condition marked by high blood sugar levels, and it is classified into several types: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes. Each type has different causes and management strategies (healthdirect).
| Diabetes Type | Description | Common Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes | Autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells | Insulin therapy, diet, and exercise |
| Type 2 Diabetes | Body’s ineffective use of insulin often linked to lifestyle | Oral medications, insulin therapy, diet, and exercise |
| Gestational Diabetes | Occurs during pregnancy and typically resolves after birth | Diet, exercise, and sometimes insulin therapy |
For more detailed information, check out our articles on endocrinology and metabolism functions and endocrine system diseases and disorders.
Understanding these endocrine disorders and their impacts on the body is essential for effective management and treatment. For further information on endocrine health and the diverse functions of the endocrine glands, visit our page on endocrine glands and their functions.
Common Endocrine Conditions
Overview of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland is overactive, producing excessive amounts of thyroid hormones T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine). This leads to a variety of symptoms and affects multiple bodily functions (healthdirect).
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Weight Loss | Unexplained weight loss despite increased appetite |
| Rapid Heartbeat | Increased heart rate or palpitations |
| Sweating | Excessive sweating or intolerance to heat |
| Nervousness | Anxiety, irritability, or shakiness |
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and energy production. Hyperthyroidism often results from conditions like Graves’ disease or toxic goiter which cause the thyroid to secrete more hormones.
Read more about the endocrine system and homeostasis for a better understanding of how hormone levels are balanced.
Impact of Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalances occur when there is too much or too little of a hormone in the bloodstream. Hormones, such as those produced by the thyroid gland, regulate crucial functions in the human body. An imbalance can significantly affect one’s health.
Common reasons for hormonal imbalance include:
- Endocrine gland dysfunction
- Stress
- Environmental factors
- Genetic predisposition
The effects of hormonal imbalance can vary widely depending on which hormones are affected. For instance, too much thyroid hormone can lead to symptoms of hyperthyroidism, whereas too little can cause hypothyroidism.
Endocrine Disorders in Daily Life
Endocrine disorders are not uncommon and can have a significant impact on daily life. Conditions such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and others result from issues within the endocrine system.
| Disorder | Description | Impact on Daily Life |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Poor regulation of blood sugar levels | Requires regular monitoring, medication, dietary adjustments |
| Hypothyroidism | Low thyroid hormone levels | Fatigue, weight gain, depression |
| Hyperthyroidism | High thyroid hormone levels | Insomnia, irritability, weight loss |
| Addison’s Disease | Insufficient adrenal hormone production | Weakness, salt craving, low blood pressure |
Testing for endocrine disorders involves checking hormone levels through blood and urine tests, as well as imaging tests to identify any anomalies such as nodules or tumors.
Find out more about endocrine disorders and treatments to understand the complexities involved in managing these conditions.
Understanding and managing these conditions effectively often requires consultation with healthcare professionals. They can ensure that hormone levels are kept in balance, thereby minimizing the impact on daily life. Regular health checkups are crucial for early detection and treatment of endocrine disorders. Explore more on the importance of health checkups in our detailed write-up.
The Endocrine System
The human body endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs responsible for hormone production and regulation. This section focuses on three key components: the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and the pancreas.
Pituitary Gland Function
The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” plays a crucial role in regulating various endocrine functions. It produces a multitude of hormones that influence other endocrine glands. Key hormones include growth hormone, which affects growth and development, and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol.
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| Growth Hormone | Stimulates growth and cell reproduction |
| ACTH | Stimulates cortisol production in adrenal glands |
| TSH | Stimulates thyroid hormone production |
| LH & FSH | Regulate reproductive processes and hormone production |
For more information on the pituitary gland and other glands, visit our article on endocrine glands and their functions.
Thyroid Gland’s Role
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones crucial for regulating metabolism. Thyroid hormones, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), influence almost every cell in the body. They regulate the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy.
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| T4 (Thyroxine) | Regulates metabolic rate and growth |
| T3 (Triiodothyronine) | Affects heart rate, metabolism, and temperature |
| Calcitonin | Helps regulate calcium levels in the blood |
Understanding the role of thyroid hormones is essential for maintaining metabolic health. For details on how these hormones interact with metabolism, refer to our page on the role of hormones in metabolism.
Significance of the Pancreas
The pancreas serves a dual role in the endocrine and digestive systems. It produces key hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which are vital for blood glucose regulation.
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| Insulin | Lowers blood glucose levels by facilitating cellular uptake |
| Glucagon | Raises blood sugar levels by promoting glucose release from the liver |
Proper functioning of the pancreas is essential for energy regulation and overall well-being. Disruptions in pancreatic hormone production can lead to conditions such as diabetes. Learn more about related conditions on our endocrine disorders and treatments page.
Understanding these components provides insight into the endocrine system and homeostasis, helping you better comprehend how hormonal balance impacts overall health. Explore more on endocrine glands functions and endocrinology and metabolism functions for a deeper dive into this complex system.
Hormonal Regulation
Understanding the mechanisms of hormonal regulation is crucial for appreciating the human body endocrine system. This section covers the role of the hypothalamus and the hormonal feedback mechanism in maintaining hormonal balance.
Hypothalamus and Hormone Control
The hypothalamus is a key brain area that links the nervous system to the endocrine system through the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland”. The hypothalamus releases hormones that help regulate the pituitary gland. In turn, the pituitary gland controls many other endocrine glands in the body.
| Gland | Function |
|---|---|
| Hypothalamus | Releases hormones that control the pituitary gland |
| Pituitary Gland | Produces hormones that regulate other endocrine glands and reduce pain through endorphins (KidsHealth) |
The hypothalamic-pituitary connection is vital for coordinating the body’s endocrine functions, impacting growth, metabolism, and stress responses. For further reading on this topic, explore endocrine system anatomy and physiology.
Hormonal Feedback Mechanism
Hormonal feedback mechanisms are pivotal in maintaining homeostasis and ensuring the body functions optimally. Hormones are chemical messengers that relay information to target cells by locking onto specific receptors (Cleveland Clinic). Too little or too much of a hormone can lead to noticeable symptoms and health issues.
The feedback system works similarly to a thermostat. When hormone levels rise above or fall below the required range, feedback signals are sent to adjust hormone production accordingly. For example, the hypothalamus detects low thyroid hormone levels and releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). TRH stimulates the pituitary to secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which then prompts the thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormones.
Understanding these mechanisms helps in managing and diagnosing various endocrine system diseases and disorders.
| Hormone | Origin | Function |
|---|---|---|
| TRH | Hypothalamus | Stimulates the release of TSH from the pituitary gland |
| TSH | Pituitary Gland | Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones |
For more in-depth insights and related topics, you can visit our articles on endocrine system and homeostasis and role of hormones in metabolism.
Seeking Endocrine Help
Understanding when and why to seek expert help is crucial for maintaining optimal health, especially when dealing with complexities of the human body endocrine system.
Role of Endocrinologists
Endocrinologists are healthcare providers specializing in the endocrine system and conditions related to hormones. They play a critical role in diagnosing and treating endocrine conditions, developing treatment plans, and prescribing medications to manage hormonal imbalances.
- Diagnosis: Endocrinologists are adept at diagnosing complex hormonal disorders through a detailed analysis of symptoms and advanced diagnostic tests. They can identify conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and adrenal insufficiency.
- Treatment Plans: Once a diagnosis is made, endocrinologists create personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s needs. This may include medication, lifestyle changes, or hormone replacement therapy.
- Pediatric Endocrinologists: Specializing in conditions affecting children under 18, pediatric endocrinologists treat growth disorders, diabetes in children, and other pediatric hormonal issues.
In certain cases, like cancer affecting endocrine tissues, care may involve collaborating with oncologists and other cancer specialists.
Importance of Health Checkups
Regular health checkups are essential for early detection and management of endocrine disorders.
| Health Checkup Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Early Detection | Regular screenings help catch hormonal imbalances and endocrine disorders early, leading to more effective treatment. |
| Risk Assessment | Individuals with a family history of endocrine system conditions, such as diabetes or thyroid disease, can better understand their risks. |
| Preventive Care | Consulting with healthcare providers helps in managing lifestyle factors to prevent the onset of endocrine-related conditions. |
| Lifestyle and Exposure Management | Endocrine disruptors found in everyday products can affect hormone balance. Managing exposure is essential to maintain endocrine health. |
Summary
Endocrinologists play a pivotal role in managing endocrine health, from diagnosing disorders to creating comprehensive treatment plans. Regular health checkups are equally critical for early detection and management of endocrine system diseases.
For in-depth information on related topics, explore our articles on:
- endocrine system diseases and disorders
- endocrine system and homeostasis
- role of hormones in metabolism
- About the Author
- Latest Posts
Johnnie D. Jackow Sr., the founder and CEO of Total Body Fitness, Worldwide, has a long-standing career in the fitness industry. He began as a certified personal trainer in the mid-90s and soon after authored his first weight loss book in 1998. This led to the launch of Total Body Fitness, Nationwide in the USA at the same time. Johnnie gained recognition as the fitness guru of his time, running infomercials on local TV late at night in Houston, Texas. Over the years, he has helped more than 40,000 individuals from all over the world achieve their health and fitness goals. With over 60,000 hours of documented training in integrative functional medicine, he completed his PhD in human physiology in 2010. His primary objective is to assist people in reaching their health and fitness goals through alternative approaches rather than relying solely on conventional medicine and pharmaceutical drugs. Today, with almost three decades of experience under his belt, Johnnie continues to be a leader in health and fitness.